스마트그리드: 에너지 전환의 미래를 선도하다
소개 기후 행동에 대한 긴급한 요구와 함께 글로벌 에너지 요구가 급증하고 있습니다.. 전통적인 전력망, 수십 년 전에 디자인되었습니다, 이 새로운 시대에 수많은 도전에 직면 해 있습니다. 스마트 그리드는 혁신적인 솔루션으로 등장했습니다, 에너지 사용을 최적화하기 위해 최첨단 기술을 통합합니다, 재생 가능 에너지 원을 수용하십시오, 그리드 신뢰성을 향상시킵니다. This article explores the key technologies, 애플리케이션, 장점, 도전, and prospects of smart grids, offering real-world examples to underline their transformative potential.
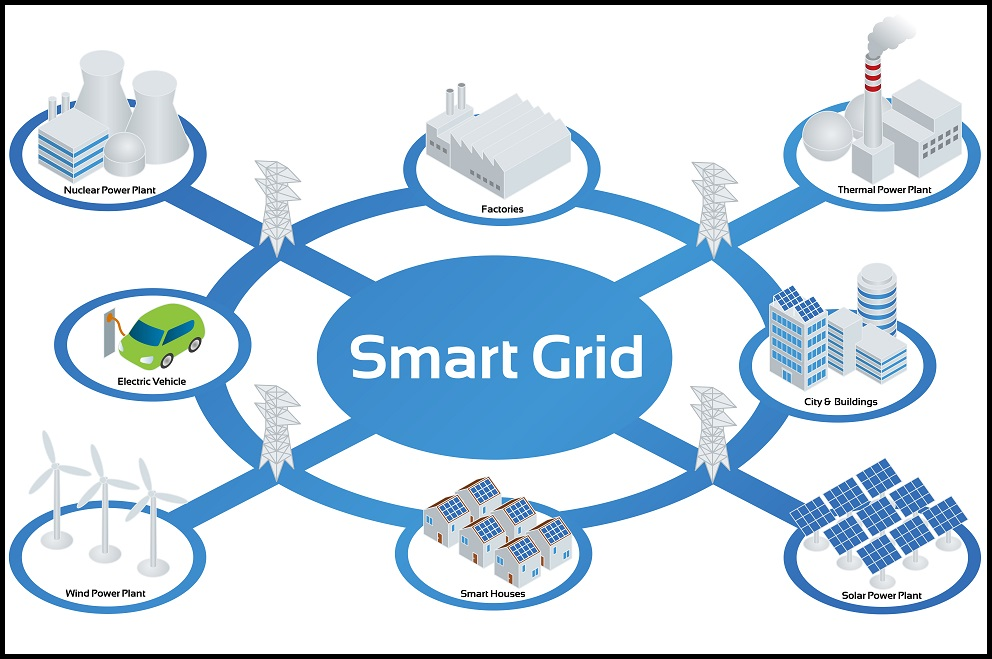
Core Technologies of Smart Grids
Smart grids rely on a blend of advanced technologies:
1. Internet of Things (IoT): IoT connects devices like sensors, 변압기, and meters to enable real-time monitoring and adjustments. 예를 들어, in the U.S., Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E) has implemented smart meters that provide instant updates on energy usage, helping consumers reduce costs and energy waste.
2. 인공 지능 (일체 포함): AI optimizes grid operations, including predictive maintenance and load forecasting. In Spain, Red Eléctrica employs AI to anticipate electricity demand and ensure efficient power distribution.
3. Energy Storage Technologies: Batteries and other storage systems stabilize the grid by storing surplus energy from renewable sources. Tesla’s “Hornsdale Power Reserve” in South Australia, one of the world’s largest lithium-ion batteries, has cut grid costs by millions annually while improving reliability.
4. Blockchain Technology: Secure and transparent blockchain systems enable peer-to-peer energy trading. Brooklyn Microgrid in New York allows residents to trade solar energy with neighbors, creating a decentralized energy marketplace.
These technologies collectively enhance the grid’s flexibility, 능률, and adaptability, supporting its ability to meet modern energy needs.


Application Areas of Smart Grids
Grid Operation and Optimization
Smart grids deploy advanced sensors and algorithms for real-time optimization. 예를 들어, Italy’s Enel has developed a smart grid platform that integrates distributed energy resources (DERs), balancing supply and demand across the nation.
Renewable Energy Integration
Integrating renewables is a cornerstone of smart grid development. Wind and 태양광 발전, though variable, can be effectively managed with advanced grid systems. Denmark exemplifies this, with over 50% of its electricity generated from wind energy, seamlessly incorporated into the grid using smart technologies.
Smart Homes and Electric Vehicles (EV)
Smart homes equipped with IoT-enabled appliances and EVs connected to charging networks demonstrate how smart grids extend to everyday life. Companies like ChargePoint have introduced dynamic charging solutions, which align EV charging times with off-peak hours to minimize strain on the grid.
Rural Electrification
In remote areas, microgrids powered by solar panels and storage units play a vital role. 예를 들어, in India, smart microgrids are helping bring electricity to villages previously off the grid, supporting economic growth and improving quality of life.
Advantages and Challenges of Smart Grids
장점
Increased Energy Efficiency: Real-time data and analytics allow for better energy distribution, minimizing losses and reducing overall consumption.
Improved Reliability: Fault detection and self-healing technologies minimize outages and speed up recovery. A notable example is the U.S. Department of Energy’s Smart Grid Investment Grant program, which has improved grid reliability across several states.
Facilitates Decarbonization: By enabling renewable energy integration and promoting energy-efficient practices, smart grids directly contribute to achieving global carbon neutrality goals.
Challenges
Significant Investment Requirements: Implementing smart grids requires substantial upfront capital for infrastructure and technology.
Technological Complexity: Coordinating a multitude of systems, from renewables to traditional power plants, requires robust interoperability standards.
Cybersecurity Risks: As digital systems grow, so does their vulnerability to cyberattacks. Enhancing grid security is an ongoing challenge that requires constant innovation and vigilance.
Global and Chinese Smart Grid Developments
Global Trends
Globally, smart grids are being embraced as the future of power systems. 국제에너지기구(International Energy Agency)에 따르면 (IEA), the smart grid market is expected to grow to $650 billion by 2025. Countries like Germany are investing heavily in smart meters and regional grid upgrades to enhance energy efficiency and reduce carbon emissions.
스마트그리드
Development in ChinaChina leads the way with its “Ubiquitous Electric Internet of Things” initiative, integrating big data, 일체 포함, and IoT into its power systems. The State Grid Corporation of China has developed an extensive ultra-high voltage (UHV) network, which efficiently transmits renewable energy across vast distances, supporting regions with high energy demand.
Smart Grids and Sustainability
Driving Green Energy Adoption
Smart grids facilitate the adoption of renewable energy by managing its inherent variability. Storage systems ensure a steady power supply even when solar or wind resources fluctuate.
Enhancing Energy Access
In developing regions, smart grids are key to achieving universal energy access. Microgrids and decentralized power systems, powered by renewables, provide a sustainable solution for electrification.
Promoting Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Smart grids contribute to several SDGs, including affordable and clean energy (SDG 7) and sustainable cities and communities (SDG 11). By reducing carbon footprints and enabling energy equity, they support global sustainability efforts.
Future Outlook for Smart Grids
Technological Innovations
Advancements in quantum computing and artificial neural networks are expected to revolutionize grid operations, enhancing forecasting accuracy and energy management capabilities.
Expanding Investment Opportunities
아시아, particularly China and India, is poised to become a major market for smart grid technologies. Initiatives like India’s National Smart Grid Mission highlight the region’s commitment to modernizing energy infrastructure.
International Collaboration
Organizations like the Global Energy Interconnection Development and Cooperation Organization (GEIDCO) are fostering cross-border energy trade and collaboration, laying the groundwork for a globally interconnected power grid.
결론
Smart grids are at the forefront of the global energy transformation, offering unparalleled opportunities to enhance efficiency, ensure reliability, and achieve sustainability. Through the integration of advanced technologies and the support of innovative policies, smart grids are poised to reshape the energy landscape for decades to come. International cooperation and investment in smart grid systems will be pivotal in realizing a resilient, sustainable energy future.
Recent Posts
폭풍과 홍수! 방수 케이블이 전력을 보호하는 방법?
최근 몇 년 동안 소개, 폭우와 홍수는 전 세계적으로 점점 더 빈번 해지고 있습니다, causing severe…
순환경제에서 케이블산업의 역할과 과제
소개 지속가능성이 글로벌 우선순위가 되면서, industries across the spectrum are reevaluating their operations…
케이블 산업이 글로벌 공급망 과제를 어떻게 충족할 수 있습니까??
글로벌 공급망은 제조업체를 연결하는 복잡하고 필수적인 네트워크입니다., 유통업체, 소매점,…
재생에너지가 케이블 수요에 미치는 영향
Introduction The global shift toward renewable energy has become a cornerstone of efforts to combat…


