Kabloyên danûstendinê yên binê avê di perestgeha têlefonê ya gerdûnî de rolek girîng dileyzin, wekî bingeha veguheztina daneya navneteweyî kar dike. Ev kablo li ser binê deryayê têne danîn, parzemînan bi hev ve girêdide û îmkana danûstendina pirfireh agahiyê li seranserê cîhanê dide. Di vê gotarê de, we will explore the technology behind submarine communication cables, how they transmit data signals, and the importance of these systems in modern communication.

Understanding Submarine Communication Cables
What Are Submarine Communication Cables?
Submarine communication cables are fiber optic cables that are specifically designed for underwater transmission of data signals. They consist of multiple optical fibers, surrounded by protective layers that shield them from environmental factors such as pressure, germî, and marine life. These cables can stretch thousands of miles across oceans, connecting cities and countries, making them essential for internet, phone, and television services.
History and Development
The first successful submarine cable was laid in 1850, initially using copper wire to transmit telegraphic messages. Over the decades, technology evolved, leading to the introduction of fiber optic cables in the 1980s. Fiber optics use light to transmit data, allowing for higher bandwidth and faster speeds compared to traditional copper cables. Îro, submarine communication cables are crucial for carrying over 95% of intercontinental data traffic.
How Submarine Communication Cables Work
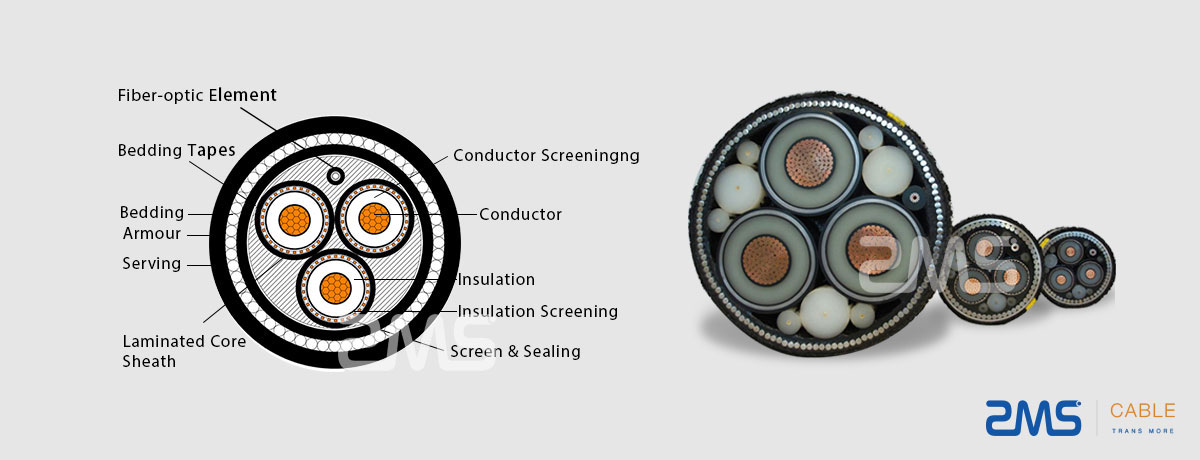
Structure of Submarine Communication Cables
Submarine cables typically consist of several layers, each serving a specific purpose:
- Navik (Optical Fibers): At the center of the cable are the optical fibers, which are thin strands of glass or plastic that carry light signals. Each fiber can transmit data at incredible speeds over long distances.
- Cladding: Surrounding the core is the cladding, which is made of a different type of glass. This layer reflects light back into the core, ensuring that the light signals do not escape and allowing for efficient transmission.
- Buffer Coating: The buffer coating protects the fibers from moisture and physical damage, providing additional strength.
- Strength Members: These are typically made of steel wires or Kevlar to protect the cable from external pressures and potential damage from fishing activities or natural disasters.
- Qîzek derveyî: The final layer is the outer jacket, which provides additional protection from the marine environment, including saltwater corrosion and abrasion.
Data Transmission Process
- Signal Generation: Data signals are generated at a transmission station, typically located on land. These signals are converted into light pulses using lasers.
- Transmission through Fibers: The light pulses travel through the optical fibers. Due to the principle of total internal reflection, the light remains contained within the core, allowing it to travel long distances without significant loss of signal.
- Repeaters: For very long distances, repeaters are placed at intervals along the cable. These devices regenerate the optical signal, amplifying it to ensure it maintains its integrity over long spans. Modern submarine cables can have repeaters every 50-100 kilometers, depending on the design and technology used.
- Reception: At the receiving end, the light pulses are converted back into electrical signals, which can then be processed by computers and other devices.
Key Technologies in Submarine Communication Cables
- Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM): This technology allows multiple data signals to be transmitted simultaneously over the same fiber by using different wavelengths (colors) of light. This significantly increases the capacity of the cable.
- Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM): An advanced form of WDM, DWDM can transmit dozens of wavelengths at once, dramatically enhancing data throughput and efficiency.
- Error Correction Protocols: To ensure data integrity, submarine cables use error correction protocols that identify and rectify any errors that may occur during transmission.
Importance of Submarine Communication Cables
Global Connectivity
Submarine communication cables connect continents and countries, facilitating global communication. They support internet services, international phone calls, and even broadcasting for television and radio networks. Without these cables, the world would be far less interconnected, and many modern conveniences would be impossible.

Economic Impact
The financial implications of submarine communication cables are profound. They support the digital economy, enabling businesses to operate efficiently across borders. The presence of reliable internet connectivity fosters economic growth, innovation, and job creation in various sectors.
Supporting Emerging Technologies
Submarine cables also enable the growth of emerging technologies, such as cloud computing, streaming services, and the Internet of Things (Iot). As more devices become connected, the demand for bandwidth increases, making robust submarine cable systems more crucial than ever.
Challenges and Considerations
Maintenance and Repair
Maintaining and repairing submarine communication cables is a complex task. Underwater environments pose numerous challenges, including harsh weather, underwater currents, and potential damage from fishing nets or ship anchors. Specialized ships equipped with advanced technology are used to locate and repair damaged cables, ensuring minimal disruption to services.
Environmental Impact
Ew installation and maintenance of submarine cables can have environmental impacts, including disruption to marine habitats. Ji ber vê yekê, careful planning and assessment are essential to mitigate these effects. Regulatory bodies often require environmental impact studies before cable projects are approved.
Security Concerns
As submarine cables carry a vast amount of sensitive data, they are vulnerable to security threats. Cyberattacks targeting these infrastructures can have catastrophic effects on global communication. Efforts are underway to enhance the security of submarine communication systems, including encryption and monitoring technologies.

Future of Submarine Communication Cables
Increasing Demand
As the world becomes increasingly reliant on digital communication, the demand for bandwidth continues to rise. Submarine communication cables will play a vital role in meeting this demand, leading to investments in new cable systems and upgrades to existing ones.
Advancements in Technology
Technological advancements are poised to enhance the capabilities of submarine communication cables. Innovations such as space-division multiplexing and quantum communication could further increase data transmission rates and security.
Sustainability Initiatives
As awareness of environmental issues grows, the industry is also focusing on sustainability. Future submarine cable projects may incorporate eco-friendly materials and methods to reduce their environmental footprint.
Submarine communication cables are a cornerstone of modern global communication, transmitting vast amounts of data across oceans and connecting people around the world. Understanding how these cables work, their significance, and the challenges they face provides valuable insights into the infrastructure that supports our digital lives. As technology continues to evolve, submarine communication cables will undoubtedly adapt to meet the growing demands of an increasingly connected world.


