The construction of global communication networks has entered a new era, particularly with the deployment of submarine cables connecting East Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and Europe. The Africa-1 cable, one of the most critical submarine communication hubs today, has successfully landed at Ras Ghareb in Egypt. This project, led by Alcatel Submarine Networks (ASN) in partnership with Egypt Telecom and several other telecom companies, aims to enhance intercontinental communications, stimulate regional economic growth, and drive the global digital transformation. This initiative is not just an infrastructure expansion; it marks a milestone in global data connectivity and communication capabilities.
Project Background and Event Overview
The Africa-1 Submarine Cable Project is a large-scale submarine cable construction project implemented by a consortium of telecom companies, including Algeria Telecom, Etisalat, Mobily, Pakistan Telecom, Egypt Telecom, and TeleYemen. The cable spans over 10,000 quilômetros, covering four continents: East Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and Europe, and is set to play a significant role in global communications. The cable’s landing in Ras Ghareb, Egito, marks the third landing point of the Africa-1 cable, after Kenya’s Mombasa and Karachi, Pakistan. This represents a major step forward for the project.
Mohamed Nasr, CEO of Egypt Telecom, stated, “The landing of the Africa-1 cable system is a landmark achievement for all involved parties, as well as for global economic development and connectivity. The system will provide more submarine routes in the growing markets of the Middle East, Asia, and Africa, improving broadband capacity and expanding our submarine network to meet the increasing demand for reliable and high-speed communication, especially for bandwidth-intensive applications like artificial intelligence.”
Originally scheduled for completion by the end of last year, the full operational launch of the Africa-1 cable is now expected in 2025. The cable is designed not only to meet current communication needs but also to accommodate future technological applications, ensuring it can adapt to the growing demands of the future.
Impact of Africa-1 Cable on Global Communications
The deployment of the Africa-1 cable significantly enhances the connectivity capabilities of multiple continents. In the context of the rapidly increasing global data traffic, Africa-1 will meet the needs for faster and more stable communication, especially in high-bandwidth scenarios.
Enhancing Regional Communication Capabilities
The deployment of the Africa-1 cable will vastly improve broadband connectivity in East Africa, the Middle East, and Asia. By offering faster and more reliable data transfer capabilities, the cable will meet the increasing demands of remote services, cross-border e-commerce, and international video conferencing in these emerging markets.
Driving Global Economic and Interconnectedness
The Africa-1 cable project not only satisfies the growing need for high-quality communication but also offers new economic opportunities for countries along its route. By connecting nations to the global economy, the cable boosts international business relations, trade, and communications. For industries heavily reliant on communication, such as finance, logistics, education, and telemedicine, the project brings new potential for growth and development.
Ensuring Data Security and Global Data Flow
Submarine cables provide long-distance, low-latency data transmission, ensuring the smooth and secure flow of global data. The Africa-1 cable’s multiple landing points system plays a critical role in mitigating cross-border network risks, thus ensuring the stability and security of communication networks, particularly in data-intensive industries.

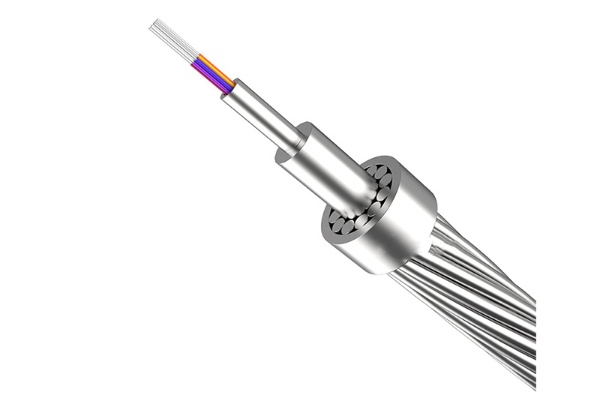
Africa-1 Cable
The successful landing of the Africa-1 cable is driven by its superior design and construction. The core of the cable consists of optical fibers, which are protected by robust layers to withstand the harsh conditions of the deep-sea environment. Below are the key technical features of the Africa-1 cable:
Eight Fiber Pairs: Supporting High-Bandwidth Applications
The Africa-1 cable is equipped with eight fiber pairs to accommodate the high-bandwidth requirements of various applications. Compared to traditional cables, the use of optical fibers enables much faster data transmission and supports bandwidth-intensive applications such as AI and the Internet of Things (IoT). This design not only satisfies current communication demands but also prepares for future technological advancements.
Multiple Landing Points: Extensive Coverage and Flexibility
The Africa-1 cable features multiple landing points, including Algeria, Djibouti, France, Kenya, Pakistan, and several Middle Eastern countries, ensuring broad coverage and flexible data transmission. This design improves data transfer efficiency across regions and connects various countries and continents in a seamless manner.
High Pressure and Corrosion Resistance: Suitable for Harsh Environments
The external structure of the cable is designed to resist corrosion, water, and pressure. This makes the cable especially suitable for underwater deployment, capable of withstanding the extreme pressures and corrosive conditions of the ocean floor, ensuring long-term stability.
Energy-Efficient and Long-Distance Signal Preservation
Compared to wireless transmission methods, the energy consumption of submarine cables is significantly lower, and the signal loss over long distances is minimal. This reduces the need for amplifiers and makes it an environmentally friendly communication medium.
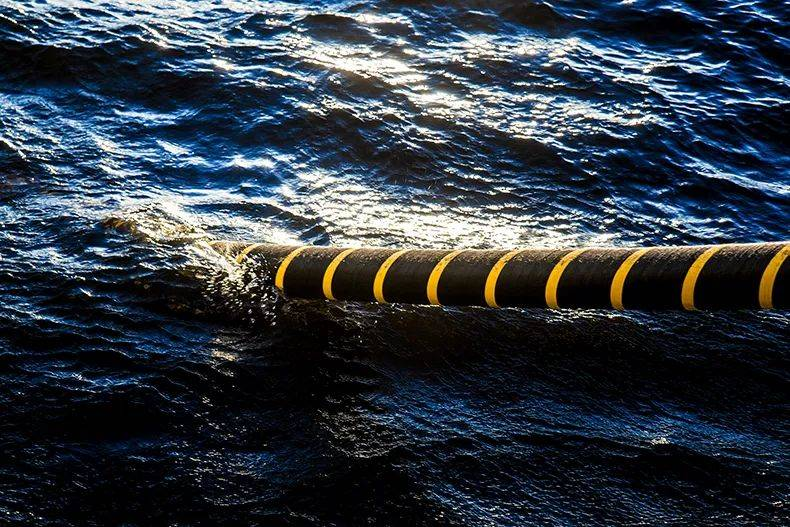

Role of Africa-1 Consortium Partners
The Africa-1 Consortium consists of multiple telecom companies, including Algeria Telecom, Egypt Telecom, Etisalat, Mobily, Pakistan Telecom, and TeleYemen, all playing crucial roles in the implementation of this project. By pooling resources, investments, and expertise, the consortium is driving the project’s progress and ensuring its successful completion.
– Egypt Telecom: As the key partner in the Ras Ghareb landing station, Egypt Telecom leads the implementation of the cable in North Africa.
– Etisalat (UAE) and Mobily: Providing funding and technical support for the Middle East connections.
– Pakistan Telecom: Facilitating the landing point in Karachi, Pakistan, ensuring seamless connectivity for South Asia.
The cooperation among these partners not only enhances the execution efficiency of the project but also facilitates the effective allocation of resources, making Africa-1 a critical addition to the global communication network.
Egypt’s Strategic Position as a Submarine Cable Hub
Egypt’s geographical location at the crossroads of Africa, the Middle East, and Europe makes it an ideal site for submarine cable landings. Ras Ghareb has become a key landing point for several important cables, including 2Africa and Red2Med, and will also host the SeaMeWe-6 cable by 2026. This strategic positioning further solidifies Egypt’s role as a global telecom hub.
A Hotspot for Submarine Cable Landings
With more than 15 submarine cables already landing in Egypt, Ras Ghareb has become a major gateway for global connectivity. This central position strengthens Egypt’s position as a pivotal player in global communications and ensures that the country remains an integral part of the global information exchange.
Addressing Geopolitical Risks and Security Concerns
The geopolitical risks in the southern Red Sea have prompted telecom companies to consider alternative submarine cable routes in the region. The Africa-1 cable, by landing in Egypt, provides a secure and stable solution to mitigate risks and ensure uninterrupted global connectivity, making it a reliable choice for telecom providers.

Supporting Future Technological Advancements
The Africa-1 cable is not only designed to meet current communication demands but also to support future technologies. Its eight fiber pairs provide robust bandwidth for emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence, big data, and 5G applications.
Supporting AI, 5G, and Other High-Bandwidth Technologies
The Africa-1 cable is a critical piece of infrastructure for supporting the demands of next-generation technologies. It enables the high-speed data transfer required for 5G networks, AI systems, and other bandwidth-intensive applications, ensuring these technologies can evolve and thrive.
Promoting IoT and Cloud Computing Adoption
The widespread coverage of the Africa-1 cable enables better data transfer for IoT devices and cloud computing services, which are key components of the global digital transformation. Its deployment ensures a more seamless and efficient data exchange, accelerating the adoption of these technologies.
Reducing Global Network Latency
The low-latency transmission capabilities of the Africa-1 cable ensure faster data exchange across continents, providing users with seamless network experiences and ensuring the smooth operation of global digital services.
Conclusão
The deployment of the Africa-1 submarine cable marks a significant achievement in global communications. This project not only improves connectivity across East Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and Europe but also provides a strong foundation for the global digital transformation. Once fully operational in 2025, Africa-1 will bring new growth opportunities for telecom providers, enterprises, and industries that rely on high-speed data transmission. Its impact will resonate across global digital economies, enabling businesses and consumers alike to benefit from faster, more reliable, and more secure communications worldwide.


